Source: Internet
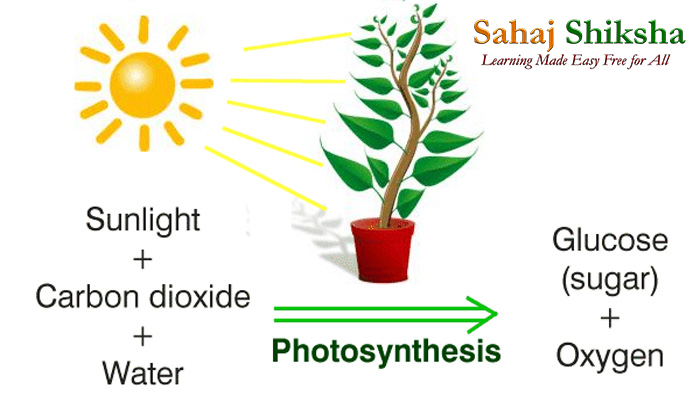
PHOTOSYNTHESIS – সালোকসংশ্লেষ
যে জৈব রাসায়নিক প্রক্রিয়ার মাধ্যমে সবুজ উদ্ভিদ কোষে সূর্যালোকের উপস্থিতিতে, পরিবেশ থেকে গৃহীত কার্বন ডাইঅক্সাইড (CO2) ও মূল দ্বারা শোষিত জলের বিক্রিয়ায় শর্করা জাতীয় খাদ্যের সংশ্লেষ ঘটে এবং গৃহীত কার্বন ডাইঅক্সাইডের সমপরিমাণ অক্সিজেন প্রকৃতিতে নির্গত হয়, তাকে সালোকসংশ্লেষ বলে।
Photosynthesis is a process by which phototrophs convert light energy into chemical energy, which is later used to fuel cellular activities. The chemical energy is stored in the form of sugars, which are created from water and carbon dioxide.
সালোকসংশ্লেষ শব্দটি দুটি গ্রিক শব্দ phos (অর্থ: আলোক; এখানে সূর্যালোক) ও synthesis (অর্থ: সংশ্লেষণ, বা তৈরি করা) এর সমন্বয়ে গঠিত।
আবার সালোকসংশ্লেষ কথাটি বিশ্লেষণ করলে দেখা যায়,সালোক শব্দটির অর্থ হলো–সূর্যালোকের উপস্থিতি এবং সংশ্লেষণ শব্দটির অর্থ—কোনো কিছু উৎপাদিত হওয়া।
এক কথায় সালোকসংশ্লেষ এর অর্থ দাঁড়ায় সূর্যালোকের উপস্থিতিতে রাসায়নিক সংশ্লেষ।
এই প্রক্রিয়ায় সজীব উদ্ভিদকোষে উপস্থিত ক্লোরোফিল নামক রঞ্জক আলোকশক্তিকে রাসায়নিক শক্তিতে রূপান্তরিত করে এবং তা উৎপন্ন শর্করাজাতীয় খাদ্যের মধ্যে স্থিতিশক্তি রূপে সঞ্চিত রাখে। এই শক্তি পরবর্তীকালে স্বভোজী উদ্ভিদ দ্বারা অথবা শাকাহারী প্রাণীদের গৌণ পুষ্টিতে সাহায্য করে। সবুজ উদ্ভিদ ছাড়া কিছু জীবাণু এবং কিছু আদ্যপ্রাণীর মধ্যেও এই প্রক্রিয়া পরিদৃষ্ট হয়। যে শারীরবৃত্তিয় জারণ-বিজারণ প্রক্রিয়ায় কিছু জীবাণু, আদ্যপ্রাণী ও ক্লোরোফিল যুক্ত সজীব কোষে (উদ্ভিদ) সূর্যালোকের উপস্থিতিতে, পরিবেশ থেকে গৃহীত কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইড ও মূলরোম দ্বারা শোষিত জলের রাসায়নিক বিক্রিয়ায় সরল শর্করা জাতীয় খাদ্য উৎপন্ন হয় ও কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইডের সমপরিমান অক্সিজেন উৎপন্ন হয় এবং সৌরশক্তির আবদ্ধ ঘটে, তাকে বা সেই প্রক্রিয়াকে সালোকসংশ্লেষ বলে। উদ্ভিদের সালোকসংশ্লেষ দিনের বেলা হয়।
The word “photosynthesis” is derived from the Greek words phōs (pronounced: “fos”) and another word pronounced as “synthesis“). Phōs means “light” and synthesis means “combining together.” This means “combining together with the help of light.”
Photosynthesis definition states that the process exclusively takes place in the chloroplasts through photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotene and xanthophyll. All green plants and a few other autotrophic organisms utilize photosynthesis to synthesize nutrients by using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. The by-product of the photosynthesis process is oxygen.
সালোকসংশ্লেষ কাকে বলে?
What Is Photosynthesis in Biology?


সালোকসংশ্লেষকে অঙ্গার আত্তীকরণ বলে কেন?
সালোকসংশ্লেষ প্রক্রিয়াকে একটি জারণ – বিজারণ প্রক্রিয়া বলা হয় কেন?
সালোকসংশ্লেষ প্রক্রিয়া উদ্ভিদের কি কি স্থানে সংঘটিত হয়?
Where Does This Process Occur?
পাতাকে সালোকসংশ্লেষের প্রধান স্থান বলা হয় কেন?
-
পাতায় ক্লোরোফিলের উপস্থিতিই পাতাকে সালোকসংশ্লেষের প্রধান স্থান করে তুলেছে।
-
পাতার ফলক অনেক চওড়া হওয়ায় সালোকসংশ্লেষের জন্য অনেকটা জায়গা পাওয়া যায়।
-
এছাড়া পাতার সজ্জাক্রম এমন হয়, যে গাছের শাখার সঙ্গে পাতার অবস্থান হয় সমকোণে। যার ফলে প্রত্যেকটি পাতা সমভাবে সূর্যালোক পায়।
পাতা ছাড়া উদ্ভিদের অন্যান্য অঙ্গ যা সালোকসংশ্লেষ করতে পারে, যেমন –
-
সদ্যোজাত উদ্ভিদের সবুজ কাণ্ড
-
লাউ, কুমড়ো ইত্যাদির সবুজ কাণ্ড
-
ফুলের সবুজ বৃতি, ফুলের সবুজ কুঁড়ি, বৃন্ত ইত্যাদি
-
গুলঞ্চর আত্তীকরণমূল
-
অর্কিডের বায়বীয়মূল
সালোকসংশ্লেষ প্রক্রিয়ার উপাদানগুলি কি কি?
- স্থলজ উদ্ভিদ তার পত্ররন্ধ্রের মাধ্যমে বায়ুমণ্ডলের কার্বনডাই অক্সাইড গ্রহণ করে।
- জলজ উদ্ভিদ জলে নিমজ্জিত অবস্থায় জলে দ্রবীভূত কার্বনডাই অক্সাইড গ্রহণ করে।
- অর্ধ নিম্মজিত উদ্ভিদ বায়বীয় অংশের দ্বারা কার্বনডাই অক্সাইড গ্রহণ করে।
Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis in plants and blue-green algae. All green parts of a plant, including the green stems, green leaves, and sepals – floral parts comprise of chloroplasts – green colour plastids. These cell organelles are present only in plant cells and are located within the mesophyll cells of leaves.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Equation
Photosynthesis reaction involves two reactants, carbon dioxide and water. These two reactants yield two products, namely, oxygen and glucose. Hence, the photosynthesis reaction is considered to be an endothermic reaction.
Following is the photosynthesis formula:
6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Unlike plants, certain bacteria that perform photosynthesis do not produce oxygen as the by-product of photosynthesis. Such bacteria are called anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria. The bacteria that do produce oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis are called oxygenic photosynthetic bacteria.
সালোকসংশ্লেষ কারী জীব
ক্লোরোপ্লাস্ট কাকে বলে | ক্লোরোপ্লাস্ট কী?
সবুজ বর্ণের প্লাস্টিডকে বলা হয় ক্লোরোপ্লাস্ট (chloroplast)। ক্লোরোফিল -a, ক্লোরোফিল -b, ক্যারোটিন ও জ্যান্থোফিলের সমন্বয়ে ক্লোরোপ্লাস্ট গঠিত। ক্লোরোফিল নামক সবুজ বর্ণকনিকা (pigment) অধিক মাত্রায় ধারণ করে বলে এরা সবুজ বর্ণের।
এতে অন্যান্য বর্ণকণিকাও কিছু কিছু পরিমাণে বিদ্যামান থাকে। উদ্ভিদের জন্য ক্লোরোপ্লাস্ট অতীব গুরুত্বপূর্ণ অঙ্গাণু। ১৮৮৩ সালে বিজ্ঞানী শিম্পার সর্বপ্রথম উদ্ভিদ কোষে সবুজ বর্ণের প্লাস্টিড লক্ষ করেন এবং নামকরণ করেন ক্লোরোপ্লাস্ট। ক্লোরোপ্লাস্ট খাদ্য সংশ্লেষে সাহায্যে করে বলে “কোষের রান্নাঘর” বা ‘শর্করা জাতীয় খাদ্যের কারখানা’ বলে। এটি শক্তির রুপান্তর অঙ্গানু।
প্রতি কোষে সংখ্যা: এক হতে একাধিক। উচ্চশ্রেণির উদ্ভিদকোষে সাধারণত ১০ হতে ৪০ টি ক্লোরোপ্লাস্ট থাকে। কিন্তু নিম্নশ্রেণির উদ্ভিদকোষে সাধারনত আরও কম থাকে।
আকৃতি: উচ্চশ্রেনির উদ্ভিদকোষে ক্লোরোপ্লাস্টের আকৃতি সাধারনত লেন্সের মতো হয়ে থাকে। নিম্নশ্রেণির উদ্ভিদে এদের আকৃতি হরেক রকম হতে পারে, যেমন- পেয়ালাকৃতি, সর্পিলাকার, জালিকাকার, তারকাকার, ফিতা বা আংটি আকৃতির, গোলাকার ইত্যাদি। শৈবালে ক্লোরোপ্লাস্টের বৈচিত্র বেশি।
আকার: লেন্স আকৃতির ক্লোরোপ্লাস্টের ব্যাস সাধারণত ৩-৫ মাইক্রন। স্প্রাইরোগাইরা এর সর্পিলাকার ক্লোরোপ্লাস্ট সোজা অবস্থায় কোষের দৈর্ঘ্যের চেয়েও বেশি লম্বা।
ক্লোরোপ্লাস্টের উৎপত্তি
নিম্নশ্রেণির উদ্ভিদে পুরাতন ক্লোরোপ্লাস্টের বিভাজনের মাধ্যমে নতুন ক্লোরােপ্লাস্টের উৎপত্তি হয়। উচ্চ শ্রেণির উদ্ভিদে আদি প্রাস্টিড হতে এদের উৎপত্তি হয়। আদি প্রাস্টিড ০.৫ মাইক্রন ব্যাসবিশিষ্ট একটি গােলাকার বস্তু। প্রতিটি আদি প্লাস্টিডে ঘন স্টোমা (ধাত্র পদার্থ) একটি দ্বিস্তরবিশিষ্ট আবরণী দ্বারা আবৃত থাকে। সূর্যালােকের উপস্থিতিতে ক্লোরােফিল সৃষ্টির সাথে সাথে আদি প্রাস্টিড পূর্ণাঙ্গ ক্লোরােপ্লস্টে পরিণত হতে থাকে।
আদি প্রাস্টিডের দ্বিস্তরবিশিষ্ট আবরণীর ভেতরের স্তর হতে ফোস্কা (vesicles) বের হয়ে আসে এবং ধাত্র পদার্থে সমান্তরালভাবে সজ্জিত হয়। এ ফোস্কাগুলাে মিলিত হয়ে একটি ল্যামেলাম তৈরি করে। কিছু কিছু স্থানে একাধিক ল্যামেলি গ্রানাম তৈরি করে কিছু কিছু ল্যামেলি বিভিন্ন গ্রানার মধ্যে সংযােগ রক্ষা করে।
এভাবে আদি প্লাস্টিড হতে সূর্যালােকের উপস্থিতিতে নতুন ক্লোরােপ্লাস্টের সৃষ্টি হয়। কিছুদিন সূর্যালােক পেলে ক্লোরােপ্লাস্ট লিউকোপ্লাস্টে পরিণত হয়, তাই সবুজ অংশ বর্ণহীন হয়
ক্লোরােপ্লাস্টের গঠন | Structure Of Chloroplast
ক্লোরোপ্লাস্ট একটি দ্বিপর্দাবিশিষ্ট অঙ্গাণু, যার বাইরের পর্দাকে বলা হয় বহিঃপর্দা এবং ভেতরের পর্দাকে বলা হয় অন্তঃপর্দা।
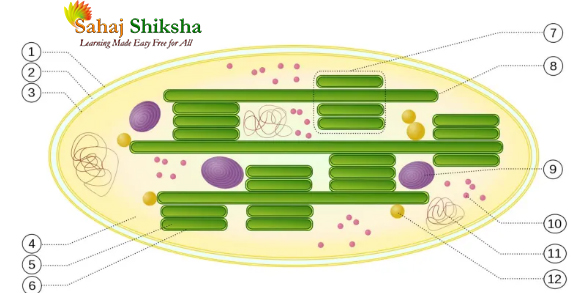
1- বহিঃপর্দা 2- পেরিপ্লাস্টিডিয়াল প্লেস
3- অন্তঃ পর্দা 4– স্টোমাটা
5- থাইলাকয়েড লুমেন 6- থাইলোকয়েড পর্দা
7- গ্রাণা 8- থাইলাকয়েড ল্যামেলি
9- স্টার্চ 10- রাইবোজোম
11- প্লাস্টিডিয়াল DNA 12- প্লাস্টোগ্লোবিউল
এই বহিঃপর্দা এবং অন্তঃপর্দার মধ্যে যে স্থান থাকে তাকে বলা হয় ‘পেরিপ্লাস্টিডিয়াল প্লেস’।
ক্লোরোপ্লাস্ট সৃষ্টির সময় অন্তঃপর্দাগুলি কোশের ভিতরে প্রবেশ করে ‘ল্যামেলি’ সৃষ্টি করে। এই ‘ল্যামেলি’ পরবর্তীকালে একটি চ্যাপ্টা উপবৃত্তাকার থলির মত অংশ সৃষ্টি করে। একে বলা হয় ‘থাইলাকয়েড’।
গ্রাণা: থাইলাকয়েড গুলো একে ওপরের উপর সজ্জিত হয়ে যে গঠন সৃষ্টি করে, তাঁকে ‘গ্রাণা’ বলা হয়।
আবার গ্রাণাগুলি যে চ্যাপ্টা পর্দাবৃত নালী দিয়ে যুক্ত থাকে তাকে ‘ল্যামেলি বা ফ্লেট’ বলে।
থাইলাকয়েড ও ল্যামেলীর মধ্যে বিভিন্ন রঞ্জক পদার্থ, এনজাইম, বাহক পদার্থ, প্রোটিন, ATPase সজ্জিত থাকে।
একটি পরিণত ক্লোরােপ্লাস্ট নিম্নলিখিত অংশগুলাে নিয়ে গঠিত।
১। আবরণী ঝিল্লি : সমস্ত ক্লোরােপ্লাস্ট একটি দুই স্তরবিশিষ্ট আংশিক অনুপ্রবেশ্য (semipermeable) মেমব্রেন (ঝিল্লি) দ্বারা আবৃত থাকে। ক্লোরােপ্লাস্ট মেমব্রেনে ফসফোলিপিড-এর পরিবর্তে গ্রাইকোসিল গ্লিসারাইড (glycosyl glyceride) থাকে। এটি একটি ব্যতিক্রমী গঠন।
২। স্ট্রোমা : আবরণী ঝিল্লি দ্বারা আবৃত পানিগ্রাহী, কলয়েডধর্মী ম্যাট্রিক্স তরলকে স্ট্রোমা (stroma) বলে। স্ট্রোমাতে 70s রাইবােসােম, অসমােফিলিক দানা, DNA, RNA, ইত্যাদি থাকে। এতে শর্করা তৈরির এনজাইমও থাকে। সালােকসংশ্লেষণে কার্বন বিজারণের মাধ্যমে শর্করা উৎপাদন প্রক্রিয়া (C3 বা C4 চক্র) স্ট্রোমাতে ঘটে থাকে।
৩। থাইলাকয়েড ও গ্রানাম : স্ট্রোমাতে অসংখ্য থলে আকৃতির 100-300 A প্রস্থ বিশিষ্ট ত্রিমাত্রিক সজ্জার গঠন বিদ্যমান। এদের থাইলাকয়েড (thylacoid) বলে। প্রত্যেকটি থাইলাকয়েডের ভেতরে একটি প্রকোষ্ঠ থাকে। এ প্রকোষ্ঠে থাকে ক্লোরােফিল-a, ক্লোরােফিল-b, জ্যান্থোফিল, ক্যারােটিন, লিপিড় ও এনজাইম। এসব বস্তুকে একত্রে স্ফটিকাকার দানার মতাে দেখায়।
তখন এদের কোয়ান্টোসােম বলে। কতগুলাে থাইলাকয়েড় একসাথে একটির ওপর আর একটি সজ্জিত হয়ে শুপের মতাে থাকে। থাইলাকয়েডের এ স্থূপকে গ্রানাম। (granum, বহুবচনে গ্রানা) বলা হয়। ১০ থেকে ১০০টি থাইলাকয়েড উপর্যুপরি । সজ্জিত হয়ে একটি গ্রানাম গঠন করে। প্রতিটি ক্লোরােপ্লাস্টে সাধারণত ৪০-৬০টি গ্রানা থাকে। একটি গ্রামের আকার ০.৩-১.৭ m (মাইক্রোমিটার)। গ্রানাম | চক্রের ঝিল্লির ভেতরের গায়ে কোয়ান্টোসােম নামক কিছু স্ফটিকার বস্তু থাকে।।
৪। স্ট্রোমা ল্যামেলি : দুটি পাশাপাশি গ্রানার কিছু সংখ্যক থাইলাকয়েডস সূক্ষ্ম নালিকা দ্বারা সংযুক্ত থাকে। এই সংযুক্তকারী নালিকাকে স্ট্রোমা ল্যামেলি (একবচনে-ল্যামেলাম) বলে। এদের অভ্যন্তরেও কিছু পরিমাণ ক্লোরােফিল বিদ্যমান থাকে।
৫। ফটোসিনথেটিক ইউনিট ও ATP-synthases : থাইলাকয়েড মেমব্রেন বহু গােলাকার বস্তু বহন করে। ইলাকয়েড মেমব্রেনের ভেতরের গাত্রে অসংখ্য সালােকসংশ্লেষণকারী একক ও ATP সিন্থেসেস নামক বস্তু থাকে।
ATP – সিন্থেসেস নামক বস্তুতে ATP-তৈরির সকল এনজাইম থাকে। মেমব্রেনগুলােতে অসংখ্য ফটোসিনথেটিক ইউনিট থাকে। প্রতি ইউনিটে ক্লোরােফিল-এ, ক্লোরােফিল-বি, ক্যারােটিন, জ্যান্থোফিল এর প্রায় ৩০০-৪০০টি অণু থাকে। এছাড়া বিভিন্ন ধরনের এনজাইম, মেটাল আয়ন, ফসফোলিপিড, কুইনােন, সালফোলিপিড ইত্যাদি থাকে।
৬। DNA ও রাইবােসােম : একটি ক্লোরােপ্লাস্টের মধ্যে সমান আকৃতির প্রায় ২০০টি DNA অণু থাকতে পারে। ক্লোরােপ্লাস্টে তার নিজস্ব বৃত্তাকার DNA ও রাইবােসােম থাকে। এদের সাহায্যে ক্লোরােপ্লাস্ট নিজের অনুরূপ সৃষ্টি (reproduce) ও কিছু প্রয়ােজনীয় প্রােটিন তৈরি বা সংশ্লেষ করতে পারে। বিজ্ঞানীদের ধারণা কোনাে আদিকোষীয় DNA ও রাইবােসােম এতে অন্তর্ভুক্ত হয়েছে।
রাসায়নিক গঠন : রাসায়নিকভাবে ক্লোরােপ্লাস্ট প্রধানত কার্বোহাইড্রেট, লিপিড, প্রােটিন নিয়ে গঠিত। এছাড়া এতে থাকে ক্লোরােফিলী প্রােটিনের মধ্যে ৮০% হচ্ছে অদ্রবণীয় যা লিপিডের সঙ্গে একত্রে ঝিল্লি নির্মাণ করে, বাকি ২০% দ্রবণীয় এবং এনজাইম হিসেবে থাকে। ক্লোরােপ্লাস্টের রয়েছে ক্লোরােফিল নামক সবুজ বর্ণকণিকা এর ৭৫% ক্লোরােফিল-a ও ২৫% ক্লোরােফিল-b এছাড়াও রয়েছে সামান্য ক্যারােটিনয়েড ও নিউক্লিক অ্যাসিড।
ক্লোরােপ্লাস্টের কাজ
(i) সালােকসংশ্লেষণ প্রক্রিয়ায় শর্করা জাতীয় খাদ্য প্রস্তুত করা ক্লোরােপ্লাস্টের প্রধান কাজ।
(i) সৌরশক্তিকে জৈবিকশক্তিতে রূপান্তর করা এবং বায়ুর কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইডকে কোয়ান্টোসােমে সংবন্ধন করা।
(iii) ক্লোরােপ্লাস্টের প্রয়ােজনে প্রােটিন, নিউক্লিক অ্যাসিড তৈরি করা।
(iv) ফটোফসফোরাইলেশন অর্থাৎ সূর্যালােকের সাহায্যে ADP-কে ATP-তে রূপান্তর করা ।
(v) ফটোরেসপিরেশন করা।
(vi) সাইটোপ্লাজমিক ইনহেরিটেন্সে সাহায্য করা।
কোয়ান্টাজোম কাকে বলে?
মনে রাখা ভালোঃ কোয়ান্টাজোমকে সালোকসংশ্লেষীয় একক বলা হয়।
সালোকসংশ্লেষের রঞ্জকতন্ত্র
সালোকসংশ্লেষের দশা বা পর্যায়
আমরা জানি সালোকসংশ্লেষের পর্যায় বা দশা দুটি দশায় বিভক্ত
1) আলোক দশা বা আলোক রাসায়নিক দশা এবং
2) আলোক নিরপেক্ষ দশা বা অন্ধকার দশা বা জৈব সালোক সালোকসংশ্লেষ দশা।
সালোকসংশ্লেষের আলোকদশা

4H2O → 4H+ + 4OH–
4OH– – 4e = 4OH
4OH = 2H2O + O2
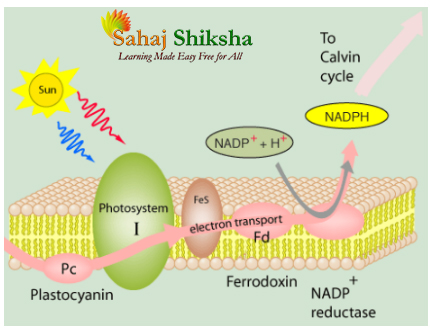
ফসফোরীভবন দু রকম হতে পারে
- আবর্তকার ফটোফসফোরাইলেশন ও
- অনাবর্তকার ফটোফসফোরাইলেশন
আবর্তকার ফটোফসফোরাইলেশন
অনাবর্তকার ফটোফসফোরাইলেশন
যে পদ্ধতিতে আলোক রশ্মি দ্বারা উদ্দিপীত জল থেকে ইলেকট্রন নির্গত হয় এবং ফটোসিস্টেম ১ এবং ফটোসিস্টেম ২ তে বিভিন্ন ইলেকট্রন বাহক দ্বারা বাহিত হয়ে NADPH এবং ATP উতপ্নন্য করে এবং অক্সিজেন নির্গমন ঘটে তাকে অনাবর্তকার ফটোফসফোরাইলেশন বলে।
সালোকসংশ্লেষের অন্ধকার দশা বা আলোক নিরপেক্ষ দশা
আলোক দশার পরর্বতী এই দশায় আলোর প্রয়োজন নেই বলে এই দশাকে আলোক নিরপেক্ষ দশা বলা হয়।
অনেকের হয়ত মনে হতে পারে এই দশাটি সূর্যের আলো থাকাকালীন হয় না, শুধু মাত্র রাতেই হয় তা কিন্তু নয়, দিনের বেলাতেও এই দশা সংঘটিত হতে পারে। আসলে আলোক দশা পরর্বতী এই দশায় আলোকের উপস্থিতি প্রয়োজন হয় না।
আলোক দশায় উৎপন্ন কি কি পদার্থ এই দশায় প্রয়োজন হয়?
আলোক দশায় উৎপন্ন ATP এবং বিজারিত NADP (নিকোটিনামাইড আডেনাইন ডাই ফসফেট) অর্থাৎ NADPH + H+ এই দশায় ব্যবহৃত হয়।
অন্ধকার দশায় কি কি ঘটনা সংঘটিত হয়?
শর্করা সংশ্লেষঃ এই অন্ধকার দশায় জৈব অণু শর্করা সংশ্লেষিত হয়। তাই এই দশাকে জৈব সংশ্লেষ দশাও বলা হয়।
অঙ্গার আত্তীকরণঃ বায়ুর কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইড এর কার্বন বা অঙ্গার এই দশায় উৎপন্ন শর্করায় অঙ্গীভূত হয়। তাই সালোক সংশ্লেষের অপর নাম অঙ্গার আত্তীকরণ।
কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইড এর বিজারণঃ এই দশায় জৈব রাসায়নিক বস্তু হিসাবে শর্করা উৎপন্ন হয়। বায়ুর কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইড বিজারিত হয়ে শর্করা উৎপন্ন করে।
NADPH এর জারণঃ আলোক দশায় উৎপন্ন বিজারিত NADP পুনরায় আলোক দশায় ব্যবহৃত হওয়ার জন্য জারিত NADP তে পরিণত হয় NADPH + H+ → NADP+
রাইবিউলুজ বিস ফসফেটের সঙ্গে কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইডের সংযুক্তির দ্বারা এই দশা শুরু হয় আর শেষ হয় পুনরায় রাইবিউলুজ বিস ফসফেটের উৎপত্তি দ্বারা। অর্থাৎ যেখান থেকে শুরু আবার সেখানেই শেষ। বার বার একই বিক্রিয়ার পুনরাবৃত্তি ঘটে চলে চক্রাকারে।
এই দশায় অঙ্গার আত্তীকরণ এর ঘটনা প্রথম পর্যবেক্ষণ করেন ব্ল্যাকম্যান(1905)। তাই এই পর্যায়কে ব্ল্যাকম্যান বিক্রিয়া বলে। কেলভিন ও বেনসন (1956) তেজস্ক্রিয় কার্বন দ্বারা এই দশার বিক্রিয়া গুলিকে বিশদ ভাবে ব্যাখ্যা করেন। তাই এদের নাম আনুসারে এই চক্রের নাম কেলভিন ও বেনসন চক্র।
কেলভিন চক্রের প্রাথমিক এনজাইমটি হল RuBisCo এর পুরো নাম হল রাইবিউলুজ বিস ফসফেট কার্বঅক্সিলেজ অক্সিজিনেজ (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) ।
চক্রটি শুরু হয় পাঁচ কার্বন যুক্ত রাইবোলোজ বিস ফসফেট সঙ্গে এক কার্বন যুক্ত কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইডের সংযুক্তির দ্বারা। বিভিন্ন যৌগ সংশ্লেষের মধ্যে দিয়ে শর্করা এবং রাইবিউলুজ বিস ফসফেট পুনরায় উৎপন্ন হয়, তাই একে চক্র বলে।
কেলভিন চক্র
কেলভিন চক্রের বিভিন্ন ধাপ
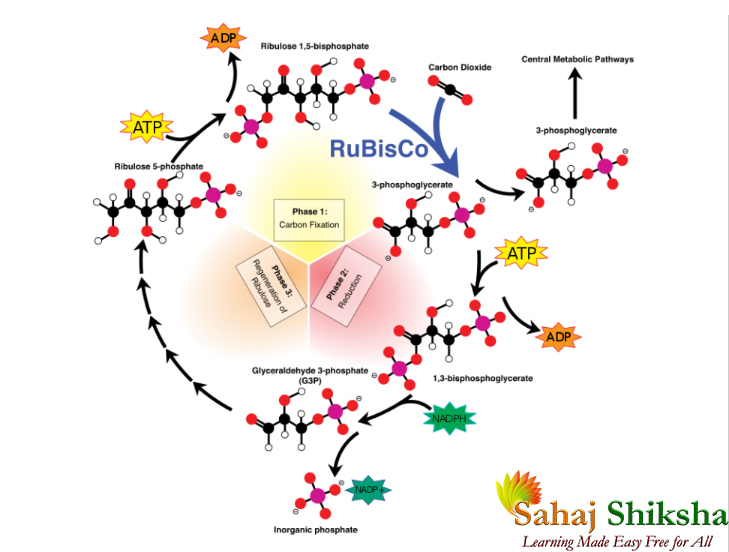
- RuBisCo উৎসেচকের সাহায্যে বাতাসের এক কার্বন যুক্ত কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইড অণু, 5 কার্বন বিশিষ্ট রাইবিউলুজ বিস ফসফেট (RUBP) অণুর সঙ্গে যুক্ত হয়ে একটি অস্থায়ী যৌগ ‘অরবিটল বিস ফসফেট’ তৈরি করে।
- এই এক অণু অস্থায়ী যৌগ ‘অরবিটল বিস ফসফেট’ থেকে কেলভিন চক্রের প্রথম স্থায়ী জৈব যৌগ তিন কার্বন যুক্ত দুই অণু ফসফোগ্লিসারিক আসিড (PGA) উৎপন্ন হয়।
- 2 অণু ফসফোগ্লিসারিক অ্যাসিড থেকে 2 অণু তিন কার্বন যুক্ত ফসফোগ্লিসার্যালডিহাইড (PGALD) উৎপন্ন হয়।
- এই ফসফোগ্লিসার্যালডিহাইড থেকে 6 কার্বন বিশিষ্ট এক অণু শর্করা (C6H12O6) উৎপন্ন হয়। এরপর কয়েকটি বিক্রিয়ার মাধ্যমে পুনরায় RUBP উৎপন্ন হয়।
- 6 অণু RUBP এর সঙ্গে 6 অণু CO2 যুক্ত হয়ে 12 অণু PGALD উৎপন্ন হয় । 12 অণু PGALD র দু অণু থেকে 1 অণু শর্করা আর বাকি 10 অণু PGALD থেকে 6 অণু RUBP তৈরি হয় এবং এই বিক্রিয়া চক্রকারে চলতে থাকে।
সংক্ষিপ্ত বিক্রিয়া পথঃ

Photosynthetic Pigments
There are four different types of pigments present in leaves:
- Chlorophyll a
- Chlorophyll b
- Xanthophylls
- Carotenoids
Structure Of Chlorophyll

A hydrocarbon tail is also present.
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in the chloroplasts of the plant cell and in the mesosomes of cyanobacteria. This green colour pigment plays a vital role in the process of photosynthesis by permitting plants to absorb energy from sunlight. Chlorophyll is a mixture of chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-b. Besides green plants, other organisms that perform photosynthesis contain various other forms of chlorophyll such as chlorophyll-c1, chlorophyll-c2, chlorophyll-d and chlorophyll-f.
Process Of Photosynthesis
At the cellular level, the photosynthesis process takes place in cell organelles called chloroplasts. These organelles contain a green-coloured pigment called chlorophyll, which is responsible for the characteristic green colouration of the leaves.
As already stated, photosynthesis occurs in the leaves and the specialized cell organelles responsible for this process is called the chloroplast. Structurally, a leaf comprises a petiole, epidermis and a lamina. The lamina is used for absorption of sunlight and carbon dioxide during photosynthesis.
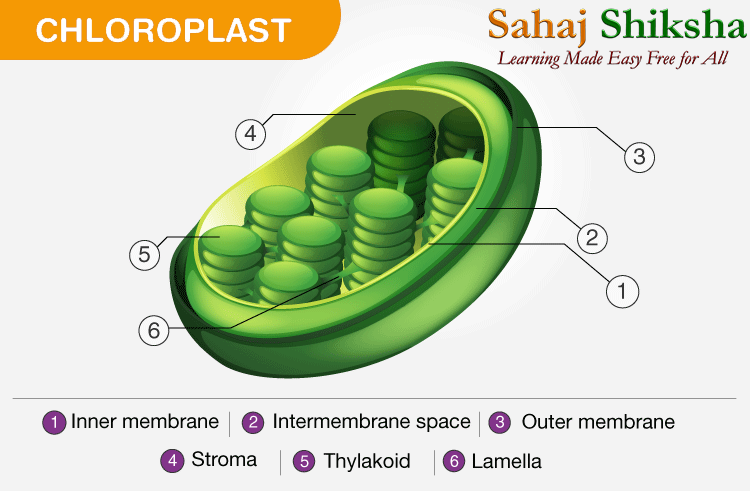
Structure of Chloroplast. Note the presence of the thylakoid
Photosynthesis Steps:
- During the process of photosynthesis, carbon dioxide enters through the stomata, water is absorbed by the root hairs from the soil and is carried to the leaves through the xylem vessels. Chlorophyll absorbs the light energy from the sun to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- The hydrogen from water molecules and carbon dioxide absorbed from the air are used in the production of glucose. Furthermore, oxygen is liberated out into the atmosphere through the leaves as a waste product.
- Glucose is a source of food for plants that provide energy for growth and development, while the rest is stored in the roots, leaves and fruits, for their later use.
- Pigments are other fundamental cellular components of photosynthesis. They are the molecules that impart colour and they absorb light at some specific wavelength and reflect back the unabsorbed light. All green plants mainly contain chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids which are present in the thylakoids of chloroplasts. It is primarily used to capture light energy. Chlorophyll-a is the main pigment.
The process of photosynthesis occurs in two stages:
- Light-dependent reaction or light reaction
- Light independent reaction or dark reaction
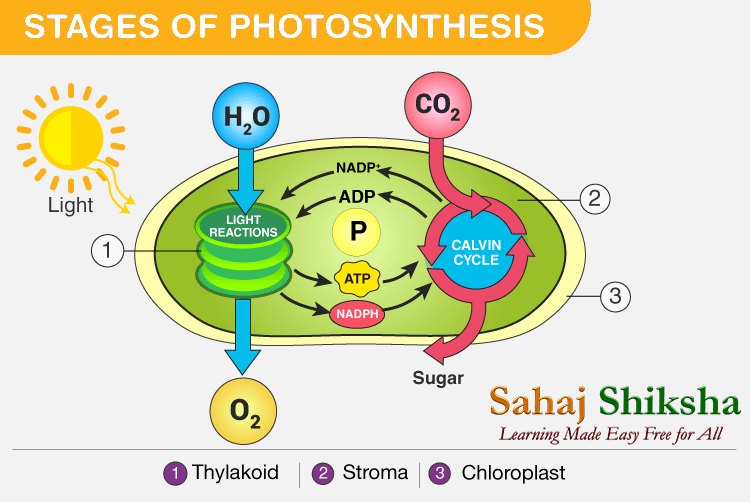
Stages of Photosynthesis in Plants depicting the two phases – Light reaction and Dark reaction
Light Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Light-dependent Reaction
- Photosynthesis begins with the light reaction which is carried out only during the day in the presence of sunlight. In plants, the light-dependent reaction takes place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
- The Grana, membrane-bound sacs like structures present inside the thylakoid functions by gathering light and is called photosystems.
- These photosystems have large complexes of pigment and proteins molecules present within the plant cells, which play the primary role during the process of light reactions of photosynthesis.
- There are two types of photosystems: photosystem I and photosystem II.
- Under the light-dependent reactions, the light energy is converted to ATP and NADPH, which are used in the second phase of photosynthesis.
- During the light reactions, ATP and NADPH are generated by two electron-transport chains, water is used and oxygen is produced.
The chemical equation in the light reaction of photosynthesis can be reduced to:
2H2O + 2NADP+ + 3ADP + 3Pi → O2 + 2NADPH + 3ATP
Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Light-independent Reaction
- Dark reaction is also called carbon-fixing reaction.
- It is a light-independent process in which sugar molecules are formed from the water and carbon dioxide molecules.
- The dark reaction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast where they utilize the NADPH and ATP products of the light reaction.
- Plants capture the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through stomata and proceed to the Calvin photosynthesis cycle.
- In the Calvin cycle, the ATP and NADPH formed during light reaction drive the reaction and convert 6 molecules of carbon dioxide into one sugar molecule or glucose.
The chemical equation for the dark reaction can be reduced to:
3CO2 + 6 NADPH + 5H2O + 9ATP → G3P + 2H+ + 6 NADP+ + 9 ADP + 8 Pi
*G3P – glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
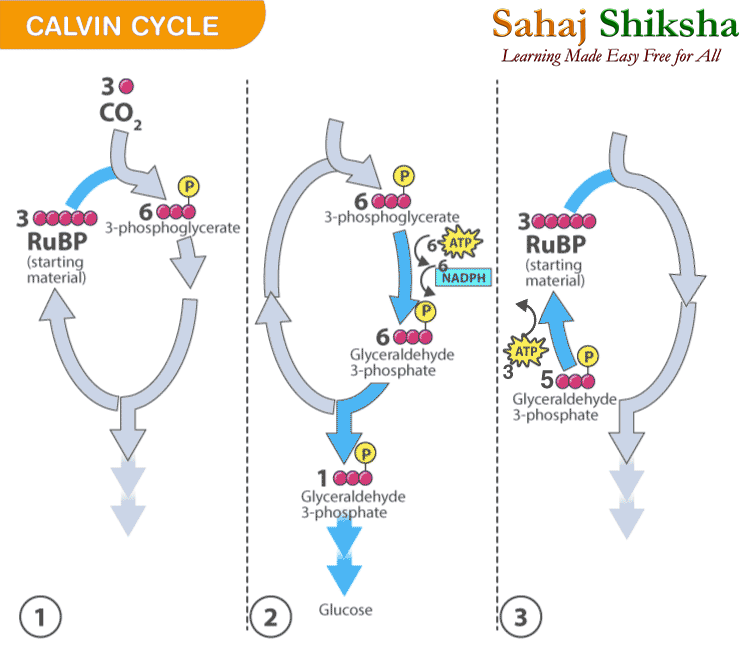
Calvin photosynthesis Cycle (Dark Reaction)
Importance of Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis is essential for the existence of all life on earth. It serves a crucial role in the food chain – the plants create their food using this process, thereby, forming the primary producers.
- Photosynthesis is also responsible for the production of oxygen – which is needed by most organisms for their survival.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is Photosynthesis? Explain the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is a biological process utilized by all green plants to synthesize their own nutrients. The process of photosynthesis requires solar energy, water and carbon dioxide. The by-product of this process is oxygen.
2. What is the significance of Photosynthesis?
During photosynthesis, oxygen gas is liberated out into the environment and is utilized by humans, animals and other living species during the process of respiration.
3. List out the factors influencing Photosynthesis.
There are several factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis. Light intensity, water, soil pH, carbon dioxide concentration, temperature and other climatic conditions are the main factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis.
4. What are the different stages of Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis takes place in two stages, namely light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions. Light-dependent reactions are also called light reactions and occur during the day time. Light-independent reaction is also called the dark reaction or the Calvin cycle.
5. What is the Calvin Cycle?
The Calvin cycle is also called the light-independent reaction. The complete process of the Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
6. Write down the Photosynthesis Equation.
6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Video Representation
![]()
